Websites
The objective is to find out what different sorts of websites are available on the internet and what makes them different from each other.
Below you can find some useful information in the format of infographics, charts and links.
Please read all information presented below, process it and then start working on the assignment
Because we are talking about websites, the link to e-commerce is pretty obvious. E-commerce is every sort of internet presence done by a company.
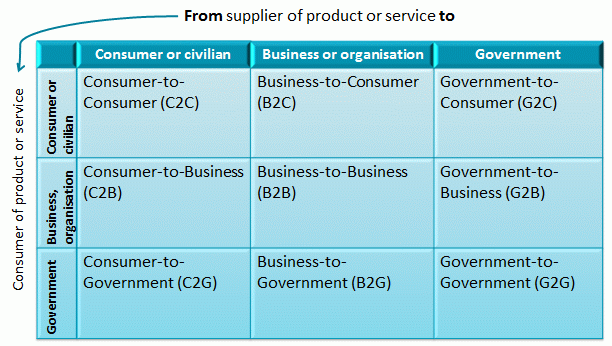
e-Commerce transaction models (x2x) and website classification
Below the picture shows the different types of e-commerce parties that can be involved in e-commerce. You notice the classic B2C, B2B one, but also C2C, C2B (web markets). And also variations where the government is one of the parties
Let's walk the different combinations:
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C).
Auction websites such as eBay, Kapaza,, etc. where consumers can sell and buy products from each other. But also product recommendations (e.g.: http://www.theSIMPLEmoms.com) from consumer to consumer. Blogs, social networks and communities can also be considered C2C
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
In many cases the classic web shop selling to consumers (transactional). But that’s not necessarily the case, e.g. the Kraft case with its relationship/brand building
Government-to-Consumer (G2C).
Automated request processes enabling consumers to request a service from the local, the central government. E.g.: TaxonWeb, an application to enter your taxes. Many communities have an “e-teller”, removing the need for a physical visit to your town hall.
Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
C2B is about an online exchange where consumers do themselves approach providers on the web.
Prospective buyers name their own price and leave it to the provider to accept or reject the offer. Can be a group of buyers (co-buy sites) e.g. to get the best heating fuel offer.
Consumer feedback can provide serious added value for an e-commerce site. A review is a powerful means to convince potential buyers. (customer review sites).
Campaigns where consumers organize themselves to influence a business (behaviour) (e.g. e-petition confronting BP, TEPCO (Fukushima nuclear plant operator)
Business-to-Business (B2B)
Setting up e-commerce towards your business customers can be a great trick to stimulate a lasting business relationship. Think of application domains such as wholesale, cloud service providers addressing the professional market, e.g. with SaaS ERP, CRM, mass e-mailing, business e-mail & collaboration, Online printers, Online accounting service provider, etc.. And of course all those “webshops” addressing the professional customers. Businesses such as BP or Dell have products that address both consumer and businesses. Different partitions of their website will be equipped to address those different target groups. Product offering will also typically differ. (e.g. more design styled consumer products compared to more robust business products).
Real life examples:
- MagCloud: B2B & B2C mix - an on demand magazine printing service. Magcloud is a B2B+B2C marketplace for on demand magazine printing: The B2B function is to offer a direct printing magazine functions. The magazine is printed on a digital printer on demand by individual order placed by consumers. So for the business wanting to publish a magazine, the issue of minimum printing run using classic printing is removed, as well as all risk of unsold stock
- MarketDojo: B2B reverse auction system. This is e-business sweets for your procurement department: the software and process to help you squeeze your suppliers to go for the lowest price possible.
- Dell:The Dell website offers B2B, B2G, B2C functionality in it’s shop. It sells products and services, and also provides e-business functions without financial transaction, such as technical support. Have a close look to its supports pages. You will find functionality such as
- Self help with “Free Hardware diagnostics, “Free Performance Diagnostics”
- Top Solutions
- Access to service desk functions
- Assisted search, using a wizard
- Order tracking
Government-to-Business (G2B)
Request automation from business to government (replacing a paper procedure or having to visit a government office) Tax entry. Fulfilling regulatory compliance processes.
Consumer-to-Government (C2G)
Pressure groups, political/social action to influence government. E-petitions
Business-to-Government (B2G)
Feedback to government businesses and non-governmental organizations.
Government-to-Government (G2G)
Local government making requests to central government (e.g. project funding,...), exchanging information, inter government services



